Recommendation Info About How To Diagnose Addison's Disease

See your doctor if you have common signs and symptoms of addison's disease, such as:
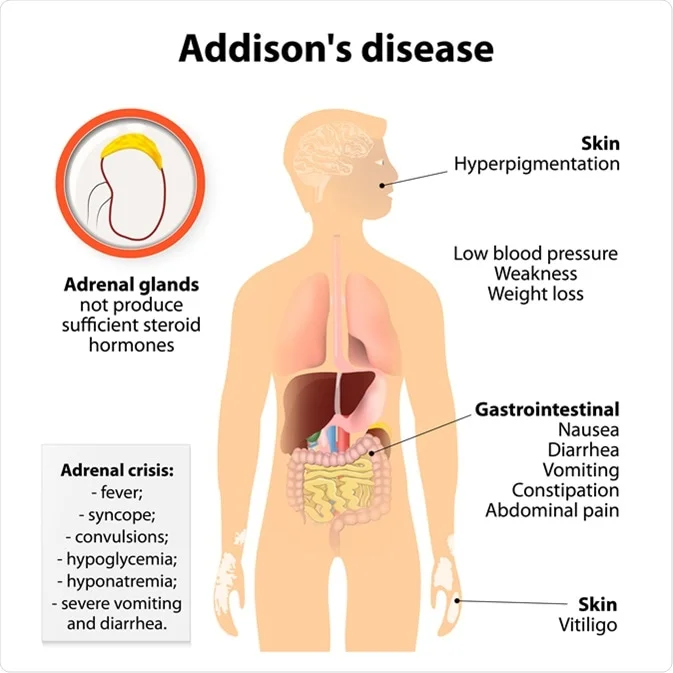
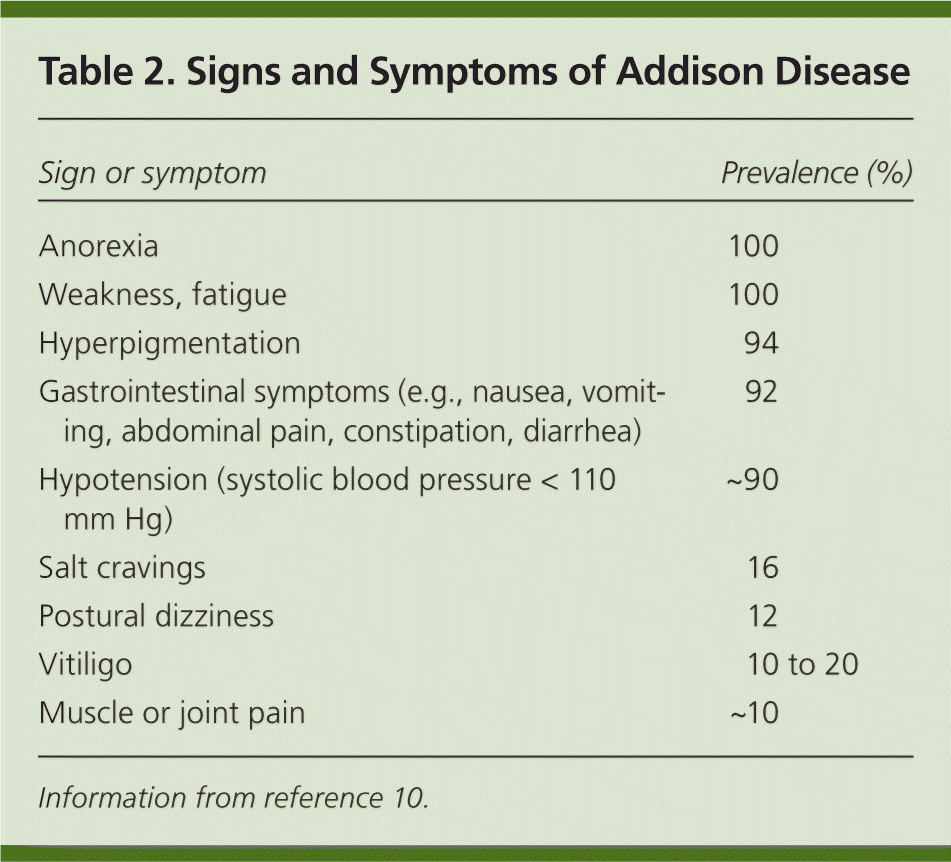
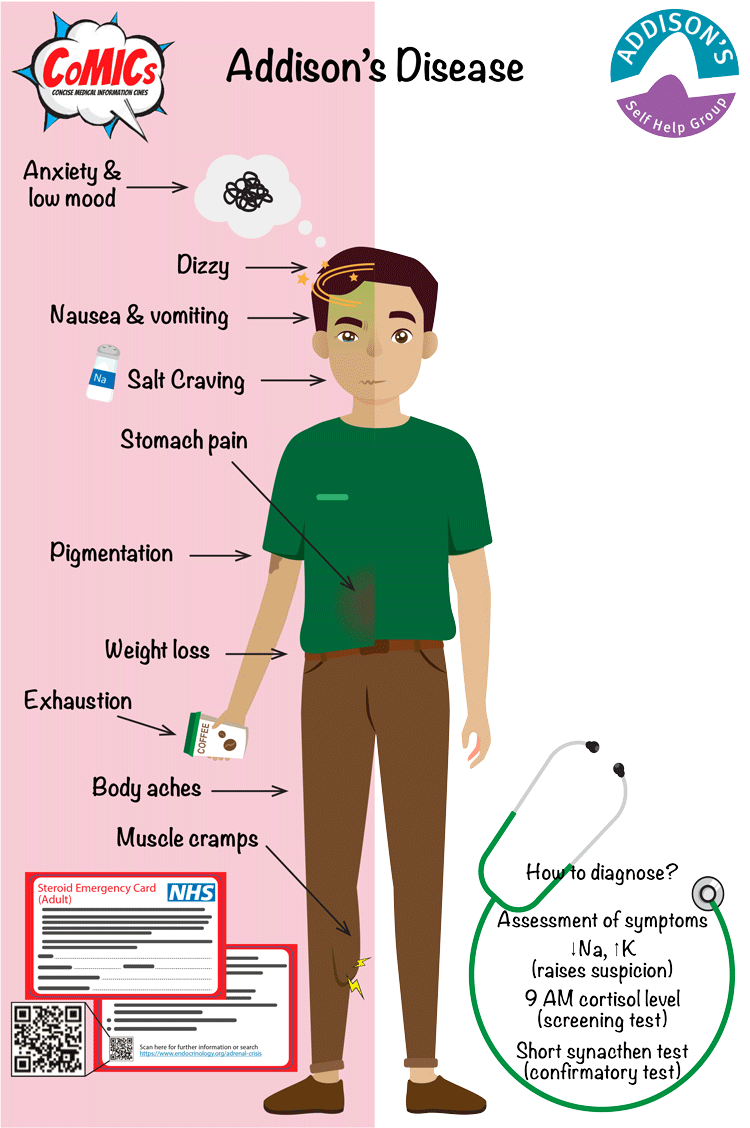
How to diagnose addison's disease. Addison disease is classically seen with hyperpigmentation due to acth melanogenesis. Symptoms of addison's disease include: Intraorally pigmentation over the gingival, vermillion border of lip, buccal mucosa, palate.
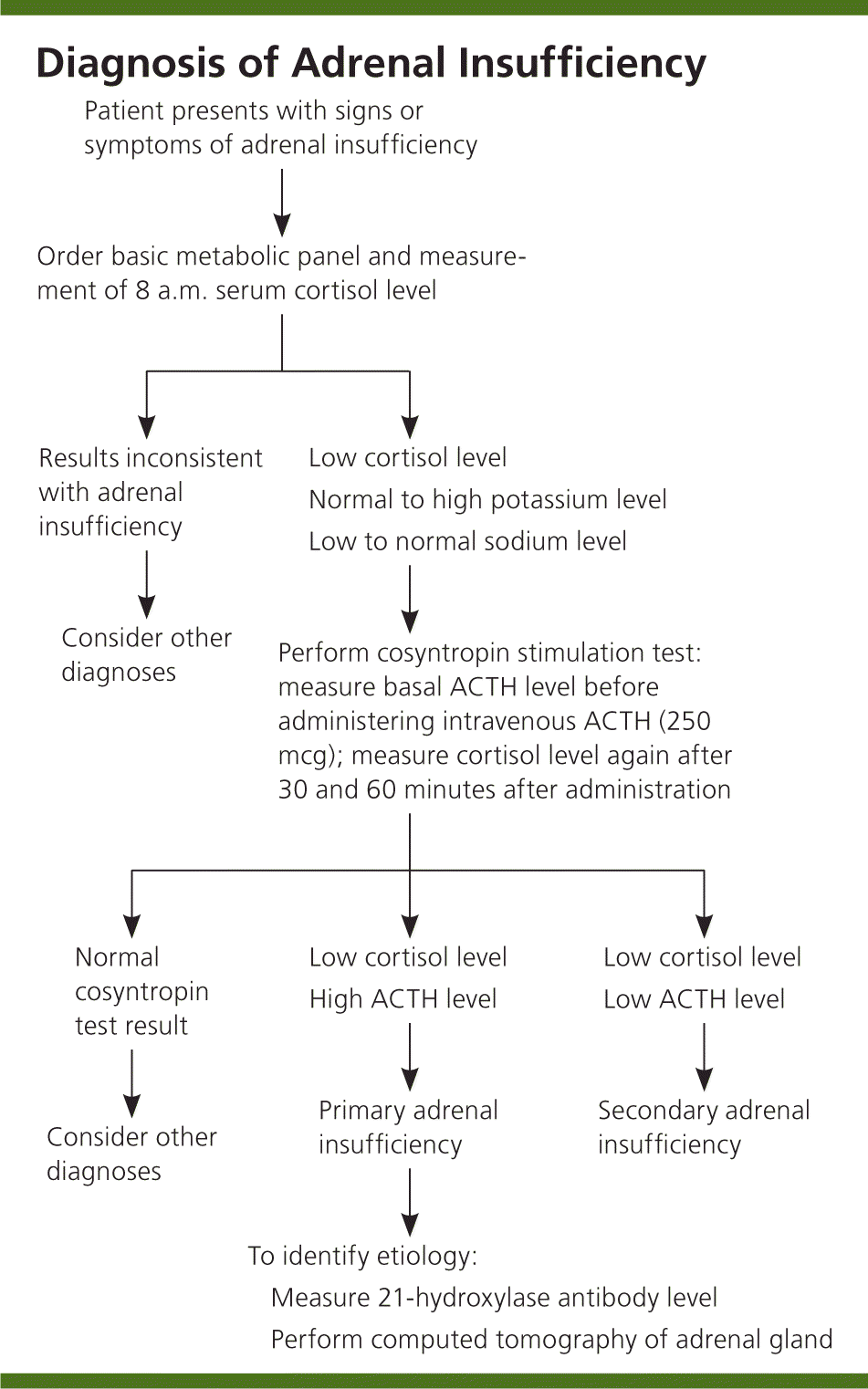
The recommended dosage is 0.1 milligrams per 10 pounds. To determine if you have addison’s disease, your healthcare provider may order the following tests: A low sodium, high potassium or low cortisol level may.
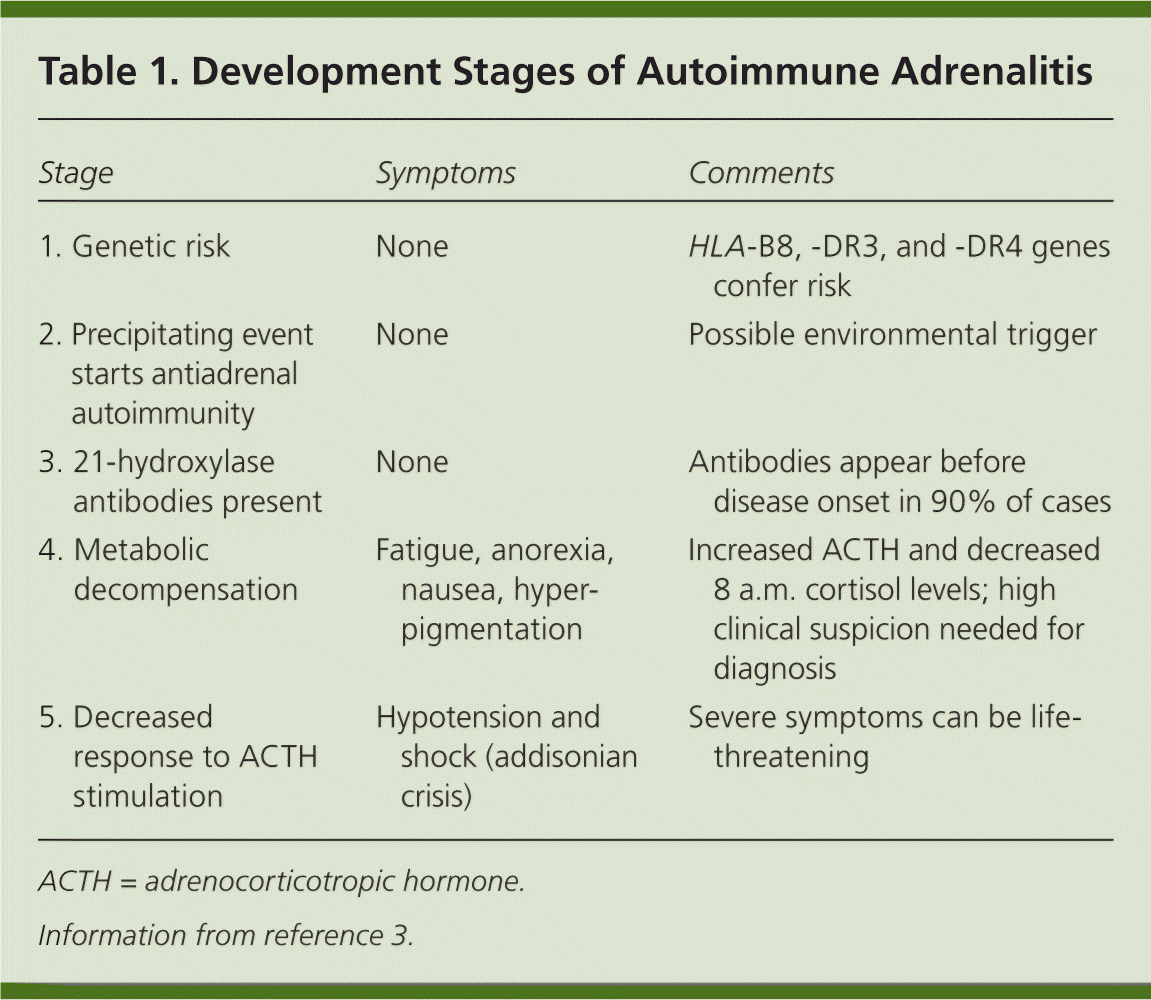
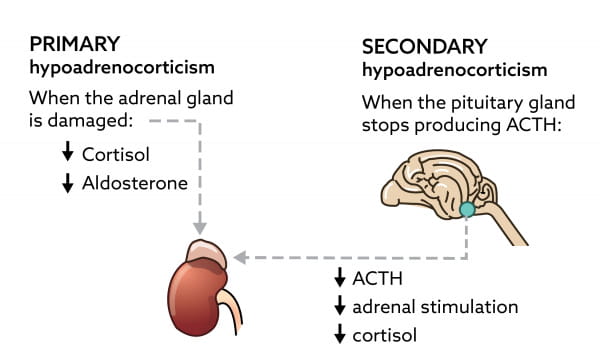
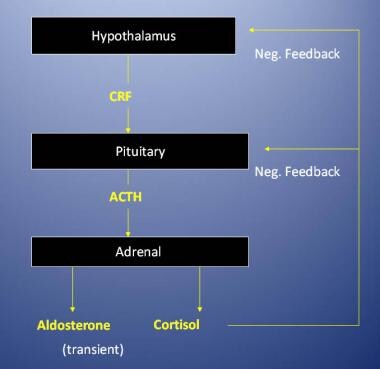
Review the individual’s medical history, ask if any close relatives have an autoimmune disorder, ask about symptoms, when. Addison's disease in dogs is often suspected after a vet listens to your observations, as. Findings of high serum adrenocorticotropic hormone (acth) and renin, as well as low cortisol and aldosterone levels, helped establish a diagnosis of addison's disease.
Diagnosing addison’s disease, your veterinarian will perform a series of blood and urine tests, looking for signs of addison’s disease. The health care provider will order blood and urine laboratory tests and measurements of adrenal hormones. To diagnose addison’s disease, a doctor will:
These include anemia, high potassium. According to a member of the dog health guide online forum, the costs for treating a basset hound with. What tests will be done to diagnose addison’s disease?
A diagnosis of addison’s disease is suspected based upon a thorough clinical evaluation, a detailed patient history and identification of characteristic findings. Addison disease is usually diagnosed after a significant stress or illness unmasks cortisol and mineralocorticoid deficiency, presenting as shock, hypotension, and volume depletion. Rarely difficult cases require additional testing.
/addisons-disease-symptoms-cause-diagnosis-treatment-4172782_FINAL-5c4550a546e0fb0001420c10.png)